LED Panel vs Traditional Lighting: Pros and Cons is a structured guide for commercial business owners and facility managers to understand how LED panel lighting stacks up against traditional lighting. It covers practical insights on efficiency, costs, quality, and future trends to support informed decision‑making.
Evaluate Your Lighting Needs for Commercial Use
Effective lighting starts with understanding your environment. Different commercial spaces—like retail stores, offices, and healthcare facilities—have unique requirements. Good lighting can boost sales in retail settings by up to 30%, reduce eye strain in offices, and improve patient comfort in healthcare areas. Smart lighting, which reacts to occupancy and daylight, can cut energy use further and lower bills. When planning, consider:
Types of lighting:
- Ambient for general illumination
- Task for focused work areas
- Accent for highlighting displays or artwork
Natural light: Use windows or skylights to improve mood and well‑being.
Standards and regulations: Follow ANSI, IES, and NFPA guidelines, especially in healthcare and industrial settings.
Placement and layering: Position fixtures to avoid glare and dark spots.
Technology: Adaptive systems adjust output based on live conditions, maximizing comfort and savings.
Understanding Business Lighting Requirements
Each commercial sector needs tailored solutions:
- Retail: Bright, even light enhances product appearance and can increase sales.
- Offices: Adjustable task lighting promotes focus; studies link good lighting to productivity gains.
- Restaurants: A mix of warm ambient and accent lights creates inviting atmospheres.
- Warehouses: High‑bay fixtures must meet safety luminance levels for efficient operations.
- Healthcare: Specific lux requirements in patient rooms and operating theaters support care quality.
- Schools and wellness centers: Daylight integration boosts concentration and well‑being.
- Outdoor areas: Durable fixtures must meet local safety codes while improving curb appeal.
Key Considerations for Choosing Lighting Solutions
Before choosing, evaluate:
- Business environment: Match light type to activities—e.g., retail needs high visibility, hospitality prefers warmer tones.
- Energy efficiency: LEDs can cut energy use by up to 85% compared to traditional options.
- Color temperature: Cooler whites (5000–6500K) aid focus; warmer whites (2700–3000K) create cozy settings.
- Maintenance demands: Review bulb lifespans and replacement schedules.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensure fixtures meet relevant ANSI, IES, and NFPA standards.
- Flexibility: Dimming and color‑tuning features adapt to changing needs.
- Smart integration: Look for compatibility with sensors and building management systems.
Compare LED Panel Lighting and Traditional Lighting
As businesses push for sustainability, comparing LEDs to traditional lighting becomes essential.
LED panels deliver 40–85% energy savings and can last 25 times longer than incandescent or fluorescent lamps. They produce less heat, reducing HVAC loads, and often offer a Color Rendering Index (CRI) above 80, crucial for accurate color work in galleries or retail. Many LED panels fit existing fixtures, simplifying retrofits. Case studies show businesses cutting annual lighting costs by up to 60% and improving worker comfort.
OLAMLED’s LED panel lights boast a CRI of 90+, ensuring more accurate color reproduction.
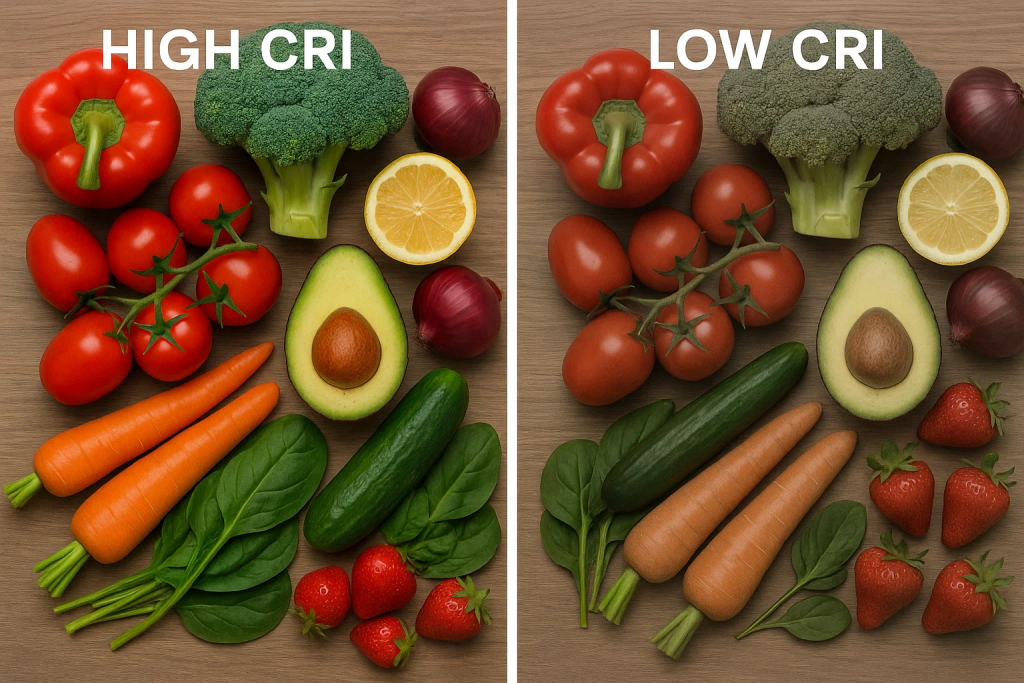
Differences in Light Quality and Output
Spectral output: LEDs offer customizable spectra; traditional bulbs emit fixed, narrower spectra. High CRI LEDs render colors more accurately, essential for visual tasks.
Heat emission: LEDs generate minimal heat, lowering cooling costs; traditional lights can waste 80–90% of energy as heat.
Durability: LED panels resist shocks and cycling; fluorescents and incandescents wear out faster under frequent on‑off conditions.
Flicker: LEDs with quality drivers have low flicker rates, reducing eye fatigue and boosting concentration.
Adaptability: Dimming and color‑tuning are standard in LEDs, but rare and less efficient in traditional systems.
Energy Efficiency: A Critical Factor
- Lumens per watt: LEDs achieve up to 160 lm/W, while incandescent bulbs manage 10–17 lm/W.
- Cost savings: Switching to LEDs can reduce energy bills by 40–85%, often paying for themselves within 3–5 years.
- Certifications: Look for ENERGY STAR or DLC listings to ensure genuine efficiency and quality.
- Environmental impact: Widespread LED use could cut national lighting costs by $30 billion annually and lower carbon emissions.

Lifespan and Durability of Lighting Solutions
- LED panels: 50,000+ hours, gradual lumen depreciation, resistant to frequent switching.
- Incandescents: 1,000–2,000 hours, sudden burnout.
- Fluorescents: 7,000–15,000 hours, sensitive to temperature and cycling.
- Maintenance impact: Longer LED life means fewer replacements, less labor, and lower material waste—key for retail and healthcare.
Cost Considerations and Return on Investment
- Upfront costs: LEDs typically cost more initially (e.g., $20–$50 per panel vs. $5–$10 for an incandescent).
- Energy and maintenance savings: Up to 85% lower bills and 25× longer life offset higher initial prices.
- Incentives: Many regions offer rebates or tax credits for LED upgrades.
- Installation expenses: Labor for retrofits can vary; planning a phased rollout can minimize disruption.
- Case studies: Businesses report ROI within 2–4 years and ongoing annual savings of 20–40%.
Examine the Benefits of LED Panel Lighting
LED panels shine in several areas:
- Energy efficiency: Cut consumption by up to 85%, reducing CO₂ emissions by millions of tons.
- Longevity: Last 25× longer, lowering replacement costs and environmental waste.
- Low heat output: Improve comfort and decrease cooling demands.
- High‑quality light: Consistent brightness, high CRI, and minimal flicker support productivity.
- Design flexibility: Slim profiles fit modern interiors; varied sizes suit offices, retail, and hospitality.
- Smart readiness: Seamless integration with IoT controls for scheduling, occupancy sensing, and daylight harvesting.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
- Reduced carbon footprint: Switching to LEDs can save roughly 11 million metric tons of CO₂ annually in the U.S.
- Hazardous materials: LEDs contain no mercury, easing disposal and recycling.
- Resource savings: Fewer replacements mean less manufacturing demand and landfill waste.
- Smart controls: Automated dimming and scheduling further boost efficiency in buildings.
Maintenance Costs and Operational Efficiency
- Lower labor needs: With up to 50,000 hours of service life, LEDs require fewer on‑site visits.
- System reliability: Robust LED panels withstand temperature extremes and vibration.
- Reduced cooling loads: Minimal heat output extends HVAC lifespan.
- Smart diagnostics: IoT‑enabled fixtures can report failures and usage data, optimizing maintenance schedules.

Smart Lighting Systems and Integration
- Energy management: Occupancy and daylight sensors adjust output, cutting energy use by up to 85%.
- User control: Remote scheduling via apps or voice commands enhances convenience and satisfaction.
- Platform compatibility: Works with Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and major home/building automation systems.
- Advanced features: Scene setting, color tuning, and security lighting add value beyond basic illumination.
Explore the Limitations of Traditional Lighting
Traditional lighting comes with drawbacks that can undermine efficiency and comfort:
- High energy use: Incandescents need 60–100 W for similar output as 10–15 W LEDs.
- Energy loss as heat: Up to 90% of power is wasted, driving up cooling costs.
- Short lifespan: Incandescents last under 2,000 hours; fluorescents up to 15,000 hours.
- Flicker and glare: Can cause eye strain, headaches, and decreased productivity.
- Environmental concerns: Fluorescents contain mercury; disposal regulations increase handling costs.
- Limited control: Smart integration is often costly or complex compared to LEDs.

Energy Consumption and Efficiency Drawbacks
- Lumens per watt: Traditional lights deliver 10–17 lm/W; LED luminous efficacy of over 100 lm/W.
- Heat generation: Traditional bulbs emit 80–90% of energy as heat versus 20% for LEDs.
- Lifespan impact: More frequent replacements increase both material and labor consumption.
- Operational costs: Higher electricity bills—up to 60% more than LED‑equipped spaces.
- OLAMLED’s LED panel lights deliver up to 160 lm/W., use 40–85% less power
Shorter Lifespan and Higher Replacement Rates
- Incandescent bulbs: 750–2,000 hours, high burnout rates.
- Fluorescent tubes: 7,000–15,000 hours, sensitive to on‑off cycling.
- Cost impact: Frequent purchases and installations drive up total cost of ownership.
- Environmental waste: More bulbs in landfills; greater resource extraction for manufacturing.
Making an Informed Decision for Your Business
Choosing the right lighting requires a clear process:
- Assess specific needs: Match light type and color temperature to your setting—warm for dining, cool for task areas.
- Research options: Compare LED, fluorescent, and incandescent across metrics like energy use, lifespan, and upfront cost.
- Layout planning: Ensure fixtures deliver uniform light and support human‑centric designs that mimic natural cycles.
- Sustainability: Factor environmental goals and corporate responsibility into your choice.
- Professional input: Consult lighting designers and electricians for tailored advice.
- Smart system evaluation: Balance benefits of automation against compatibility and network costs.
- Training and safety: Ensure installation teams follow NEC or local electrical code standards.
Conducting a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Identify costs: Fixture price, installation labor, infrastructure adjustments.
Quantify benefits: Energy savings, productivity gains, maintenance reductions.
Use financial models: Apply NPV or ROI calculations over expected lifespans.
Sensitivity checks: Test scenarios with varying energy prices and usage hours.
Summary table: Present payback period, lifetime cost, and productivity impact side by side.
Recommendation: Highlight the option with the best long‑term value, even if its upfront cost is higher.
Best Practices for Commercial Lighting Installation
- Detailed plan: Specify wattage, color temperature, and placement in a schematic.
- Quality components: Choose DLC or ENERGY STAR fixtures for reliability.
- Safety protocols: Train teams on NEC and lockout/tagout procedures.
- Systematic rollout: Phase installations to minimize business interruptions.
- Post‑installation checks: Use a checklist to verify performance and compliance.
- Maintenance plan: Offer clients scheduled inspections and remote monitoring options.
Future Trends in Lighting Technology
- Smart ecosystems: Greater IoT integration for energy insights and predictive maintenance.
- Tunable and human‑centric lighting: Dynamic white and color‑tuning to support circadian rhythms.
- Emerging materials: OLED panels and bio‑based LEDs for novel design and efficiency.
- Renewable pairing: Solar‑powered lighting in outdoor spaces to cut grid dependence.
- Data‑driven design: Lighting analytics guide layout changes and energy management.

LED Panel vs Traditional Lighting FAQs
What are the main advantages of LED panel lighting for businesses?
LED panels use up to 85% less energy, last 25× longer, deliver high CRI for accurate color, produce less heat, and integrate easily with smart controls—driving significant savings and better work environments.
How does the lifespan of LED lights compare to traditional lights?
LED lights typically last 15,000–50,000 hours, versus 1,000–2,000 hours for incandescents and 7,000–15,000 hours for CFLs, reducing replacement frequency and related costs.
Are LED lights more environmentally friendly?
Yes. LEDs consume up to 85% less power, contain no mercury, generate less waste over time, and can be paired with renewable energy—cutting greenhouse gas emissions and hazardous waste.
What factors should I consider when evaluating lighting costs?
Consider fixture price, energy efficiency (lm/W), installation labor, maintenance schedules, lifespan, and any available rebates or tax incentives to calculate total cost of ownership.
Can LED panel lights be integrated with smart lighting systems?
Absolutely. Many LED panels work with Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Amazon Alexa, and Google Home, offering features like remote scheduling, automated dimming, and occupancy sensing.



